Linked-list
각 노드가 데이터와 포인터를 가지고 한 줄로 연결되어 있는 방식으로 데이터를 저장하는 자료 구조이다.
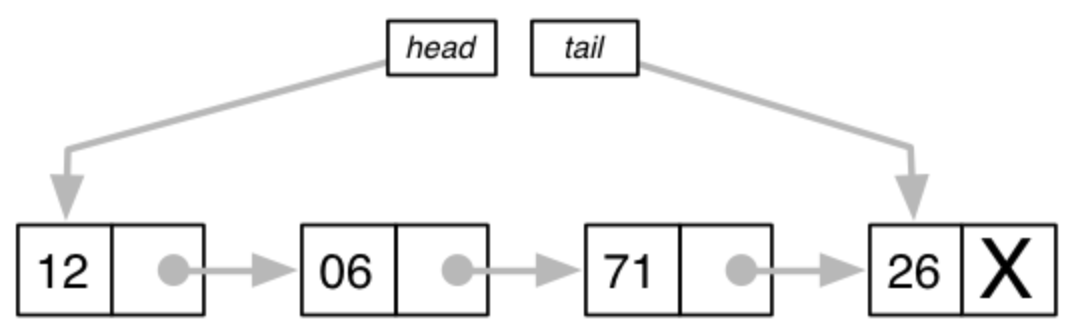
- 각각의 노드는 데이터와 다음노드가 무엇인지 알려주는 주소(링크)를 가지고 있다.
- 링크를 통해서 데이터를 추가 / 삭제 / 탐색 가능 한데, 특히 추가에 용이하다.
- 사용예시: 플레이리스트, 이미지 뷰어 등
- Singlylinkedlist, doublylinkedlist, Circularlinked lists 등이 있다.
- 저장은 차례대로지만 메모리들은 무조건적으로 연속적으로 위치하지는 않는다.
- 링크 메모리(링크 하나: 4byte)를 필요로 한다.
- 프로그램 수행시 크기가 동적으로 변화하기 때문에 메모리 공간 낭비가 적다.
링크드 리스트 VS 배열
링크드 리스트
메모리상에 원소들이 연속적으로 위치하지 않는다.
배열에 비해 데이터의 추가 / 삽입 이 용이하다.
배열에 비해 메모리를 더 효율적으로 쓸 수 있다.
특정 위치의 데이터를 검색하기 위해서 처음부터 끝까지 순회해야 한다.
추가/삭제 에 용이하다.
배열
메모리를 연속적으로 할당한다.
동일한 데이터 타입을 연속적으로 저장할 수 있다.
(찾기)탐색이쉽다.
고정된 크기를 가지고 있어서 배열의 처음이나 중간에서 원소를 넣고 빼기 어렵다.
탐색/정렬 에 용이하다.
Linked-list 구현하기 (singly linked list)
1) class Node & class LinkedList
LinkedList(type: object)
- head와 tail 변수를 갖고 있으며 구현된 linked list의 처음(head)과 끝(tail) 노드를 가리킨다.
LinkedList.head(type: object)
- head 변수를 담고 있어 나중에 head를 제거할 때 쉽게 사용할 수 있다.
LinkedList.tail(type: object)
- addToTail() 메소드를 사용할 때 가장 끝에 노드를 붙일 때 사용한다.
Node(type: object)
- Node 객체를 상속 받아서 new node 를 생성 할 때마다 해당 객체를 상속 받게 된다.
Node.value (type: number)
- node를 생성할때 주어진 value 값이 저장된다.
Node.next (type: object)
- 다음 노드를 가리키는 값이 저장되어 있으며, 없을 경우에는 null 이다.
2) Methods
addToTail(value)
- Linked List의 가장 끝(tail)에 새로운 node를 추가할 때 사용할 메소드 이다.
- list.tail을 이용하여 구현한다.
remove(value)
- linked list의 가장 앞(head)를 삭제할 때 사용할 메소드 이다.
- 삭제시에 list.head 을 이용하여 구현하며 삭제 전 head의 값을 node.next 노드로 변경 한 후 기존 head node를 삭제 해야 한다.
getNodeAt(index)
contains(value)
- Linked List 로 구현된 객체에서 node.value 가 존재 하는지 확인한다.
- list.head 부터 value 값이 존재하는지 확인해야 하므로 worst case의 경우에는 모든 link를 다 봐야 하는 경우가 생긴다. ( 찾고자 하는 값이 가장 끝 노드에 위치할 경우)
- 이러한 경우 때문에 Linked List의 최악의시간복잡도 (O)는 O(n) 이 된다.
indexOf(value)
size()
본인이 작성한 코드
class Node {
constructor(value) {
this.value = value;
this.next = null;
}
}
class LinkedList {
constructor() {
this.head = null;
this.tail = null;
this._size = 0;
}
//연결 리스트의 마지막에 데이터를 추가합니다.
addToTail(value) {
if(!this.head){
this.head = new Node;
this.head.value = value;
} else {
let curNode = this.head;
while(curNode.next){
curNode = curNode.next;
}
curNode.next = new Node;
curNode.next.value = value;
}
this._size++;
}
// 해당하는 연결 리스트의 값을 지웁니다.
remove(value) {
if(!this.head) return undefined;
if(this.head.value === value){
this.head = this.head.next;
return this;
}
let preNode = this.head;
let curNode = this.head.next;
while(curNode){
if(curNode.value === value){
break;
} else {
preNode = curNode;
curNode = curNode.next;
}
}
preNode.next = curNode.next;
this._size--;
return this;
}
//인덱스를 넣었을 때, 그 인덱스가 어떠한 노드를 가지고 있는지 반환합니다.
getNodeAt(index) {
let curNode = this.head;
let ind = 0;
while(curNode){
if(ind === index){
return curNode;
}
ind++;
curNode = curNode.next;
}
return undefined;
}
//해당 값이 연결 리스트에 있는지 true와 false 로 반환합니다.
contains(value) {
if(this.indexOf(value) === -1){
return false;
}
return true;
}
indexOf(value) {
let curNode = this.head;
let index = 0;
while(curNode){
if(curNode['value'] === value){
return index;
}
index++;
curNode = curNode.next;
}
return -1;
}
//노드의 개수 반환.
size() {
return this._size;
}
}reference code
class Node {
constructor(value) {
this.value = value;
this.next = null;
}
}
class LinkedList {
constructor() {
this.head = null;
this.tail = null;
this._size = 0;
}
addToTail(value) {
const newNode = new Node(value);
if (this.head === null) {
this.head = newNode;
this.tail = newNode;
} else {
this.tail.next = newNode;
this.tail = newNode;
}
this._size += 1;
}
remove(value) {
const index = this.indexOf(value);
if (index === -1) {
return;
}
if (index === 0) {
if (this.head === this.tail) {
this.head = null;
this.tail = null;
this._size = 0;
} else {
this.head = this.head.next;
this._size -= 1;
}
return;
}
const prevNode = this.getNodeAt(index - 1);
const removedNode = prevNode.next;
if (removedNode === this.tail) {
prevNode.next = null;
this.tail = prevNode;
this._size -= 1;
return;
}
prevNode.next = removedNode.next;
this._size -= 1;
}
getNodeAt(index) {
let counter = -1;
let currentNode = this.head;
while (currentNode) {
counter += 1;
if (index === counter) {
return currentNode;
}
currentNode = currentNode.next;
}
return undefined;
}
contains(value) {
return this.indexOf(value) !== -1;
}
indexOf(value) {
let index = 0;
let currentNode = this.head;
while (currentNode) {
if (currentNode.value === value) {
return index;
}
index += 1;
currentNode = currentNode.next;
}
return -1;
}
size() {
return this._size;
}
}
(참고 블로그: velog.io/@riceintheramen/Linked-list)
hashTable
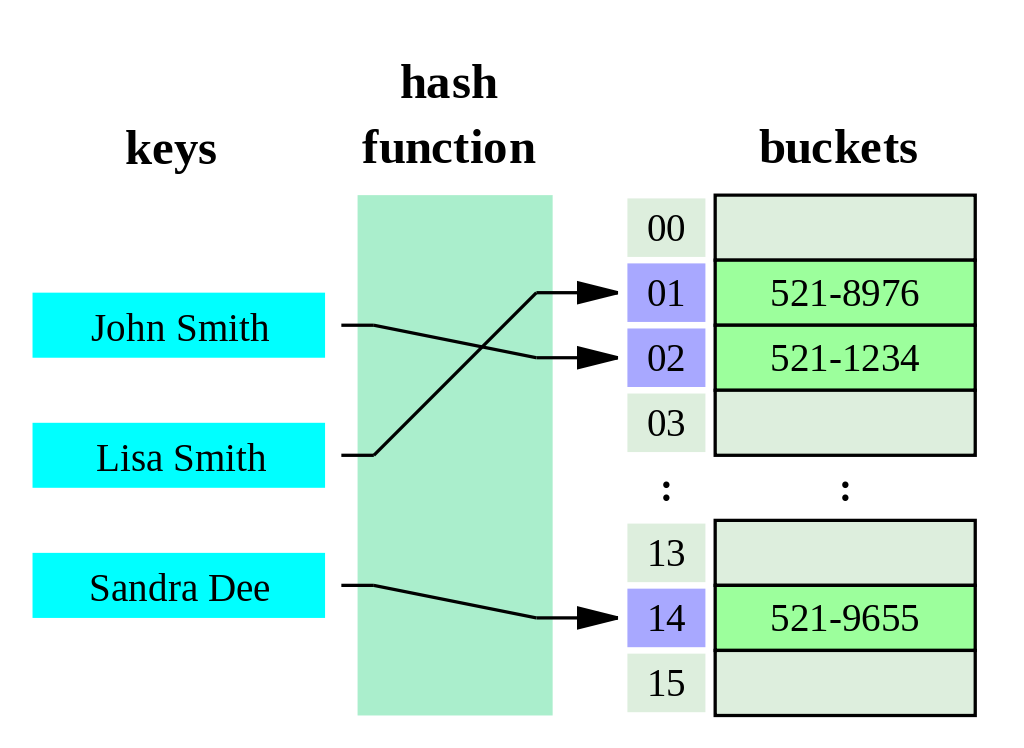
- 어떠한 키와 값을 넣으면, 내부적으로 이 데이터를 분류하여 지정된 장소에 키와 값을 넣고, 키를 재 호출하면 값을 반환할 수 있다.
- 추가/삭제/탐색이 쉽고 빠르다.(해싱된 키 => 배열의 인덱스) 배열의 인덱스를 사용하여 검색
- key 값 => hash function(해싱) => 데이터 분류 후 정수 => 인덱스가 되어 저장됨.
- 크기가 정해져 있음(크기 지정 가능)
- Hash function 과 Hash collision
Hash function
어떠한 값을 넣었을 때 정보를 암호화하거나 일련의 값으로 만들어 내는 것.
hashing? 가변 크기의 입력값(input key)에서 고정된 크기의 출력값(hash sum)을 생성하는 과정

- 배열의 크기 안에서 값이 나와야 함
- 언제든지 같은 값이 나와야 함
- 들어온 key를 저장할 수 없음
Hash collision
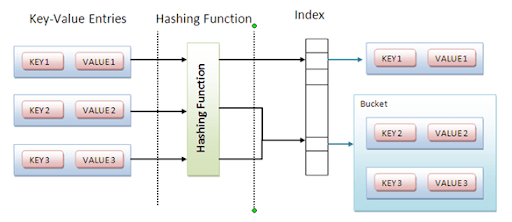
Storage 의 해당 인덱스에 Bucket을 만들어 같은 인덱스를 갖는 key-value 들을 저장해 줄 수 있다.
Hash Table 구현하기
본인이 작성한 코드
class HashTable {
constructor() {
this._size = 0;
this._bucketNum = 8;
this._storage = LimitedArray(this._bucketNum);
}
//linkedList 로 구현해보기.
insert(key, value) {
const index = hashFunction(key, this._bucketNum);
//객체 형태의 bucket을 만들어 준다.
//변수를 재할당하기 위해 let 을 사용한다.
const oldbucket = this._storage.get(index);
let bucket = {};
//기존 버킷이 존재하지 않을 경우 새로운 버켓을 만들어 storage에 넣어준다.
if(!oldbucket){
bucket[key] = value;
this._storage.set(index, bucket);
//기존 버킷이 존재할 경우, 기존 버킷에 key와 value를 넣어주는데,
//key값이 같은 경우 value가 자동으로 업데이트 된다.
} else {
bucket = oldbucket;
bucket[key] = value;
this._storage.set(index, bucket);
}
this._size++;
if(this._size > this._bucketNum*0.75){
this._resize(2*this._bucketNum)
}
return this._storage;
}
retrieve(key) {
const index = hashFunction(key, this._bucketNum);
if(this._storage.get(index)){
return this._storage.get(index)[key];
}
}
remove(key) {
const index = hashFunction(key, this._bucketNum);
// let removed = this._storage.get(index);
this._storage.load().splice(index, 1);
this._size--;
if(this._size < this._bucketNum*0.25){
this._resize(this._bucketNum/2)
}
}
_resize(newBucketNum) {
let copyStorage = this._storage;
this._bucketNum = newBucketNum;
this._storage = LimitedArray(this._bucketNum);
this._size = 0;
// copyStorage.each(obj => {
// for (let objKey in obj) {
// this.insert(objKey, obj[objKey]);
// }
// });
copyStorage.load().forEach(obj=>{
for (let objKey in obj) {
this.insert(objKey, obj[objKey]);
}
});
return this._storage;
}
}hashFunction 과 LimitedArray 는 존재한다고 가정한다.
레퍼런스 코드
class HashTable {
constructor() {
this._itemNum = 0;
this._bucketNum = 8;
this._storage = LimitedArray(this._bucketNum);
}
//단축 평가 = shortcut circuit
//초기값, 디폴트 값 설정할 때 많이 쓰는 코드.
//const bucket = this._storage.get(index) || [];
insert(key, value) {
const index = hashFunction(key, this._bucketNum);
const bucket = this._storage.get(index) || [];
for (let i = 0; i < bucket.length; i += 1) {
const tuple = bucket[i];
if (tuple[0] === key) {
const oldValue = tuple[1];
tuple[1] = value;
return oldValue;
}
}
bucket.push([key, value]);
this._storage.set(index, bucket);
this._itemNum += 1;
if (this._itemNum > this._bucketNum * 0.75) {
this._resize(this._bucketNum * 2);
}
return undefined;
}
retrieve(key) {
const index = hashFunction(key, this._bucketNum);
const bucket = this._storage.get(index) || [];
for (let i = 0; i < bucket.length; i += 1) {
const tuple = bucket[i];
if (tuple[0] === key) {
return tuple[1];
}
}
return undefined;
}
remove(key) {
const index = hashFunction(key, this._bucketNum);
const bucket = this._storage.get(index) || [];
for (let i = 0; i < bucket.length; i += 1) {
const tuple = bucket[i];
if (tuple[0] === key) {
bucket.splice(i, 1);
this._itemNum -= 1;
if (this._itemNum < this._bucketNum * 0.25) {
this._resize(Math.floor(this._bucketNum / 2));
}
return tuple[1];
}
}
return undefined;
}
_resize(newBucketNum) {
const oldStorage = this._storage;
// min size of 8, return if nothing to do!
newBucketNum = Math.max(newBucketNum, 8);
if (newBucketNum === this._bucketNum) {
return;
}
this._bucketNum = newBucketNum;
this._storage = LimitedArray(this._bucketNum);
this._itemNum = 0;
oldStorage.each((bucket) => {
if (!bucket) {
return;
}
for (let i = 0; i < bucket.length; i += 1) {
const tuple = bucket[i];
this.insert(tuple[0], tuple[1]);
}
});
}
}
'BootCamp_Codestates > IM Tech Blog' 카테고리의 다른 글
| 3-1. Inheritance Patterns - Subclassing, Prototype Chain (0) | 2020.12.09 |
|---|---|
| 3. Inheritance Patterns - Object Oriented Programming (0) | 2020.12.09 |
| 2. Data Structure - Stack, Queue (1) | 2020.12.03 |
| 1-1. IM Prep - modern JavaScript (0) | 2020.12.03 |
| 1. IM Prep - Git workflow (0) | 2020.12.03 |
