JTB
2025. 8. 17. 19:47
NAT (Network Address Translation) is a networking technique that modifies the IP address information in packet headers while the packets pass through a router or firewall.
Its primary purpose is to map private (internal) IP addresses to public (external) IP addresses, and vice versa.
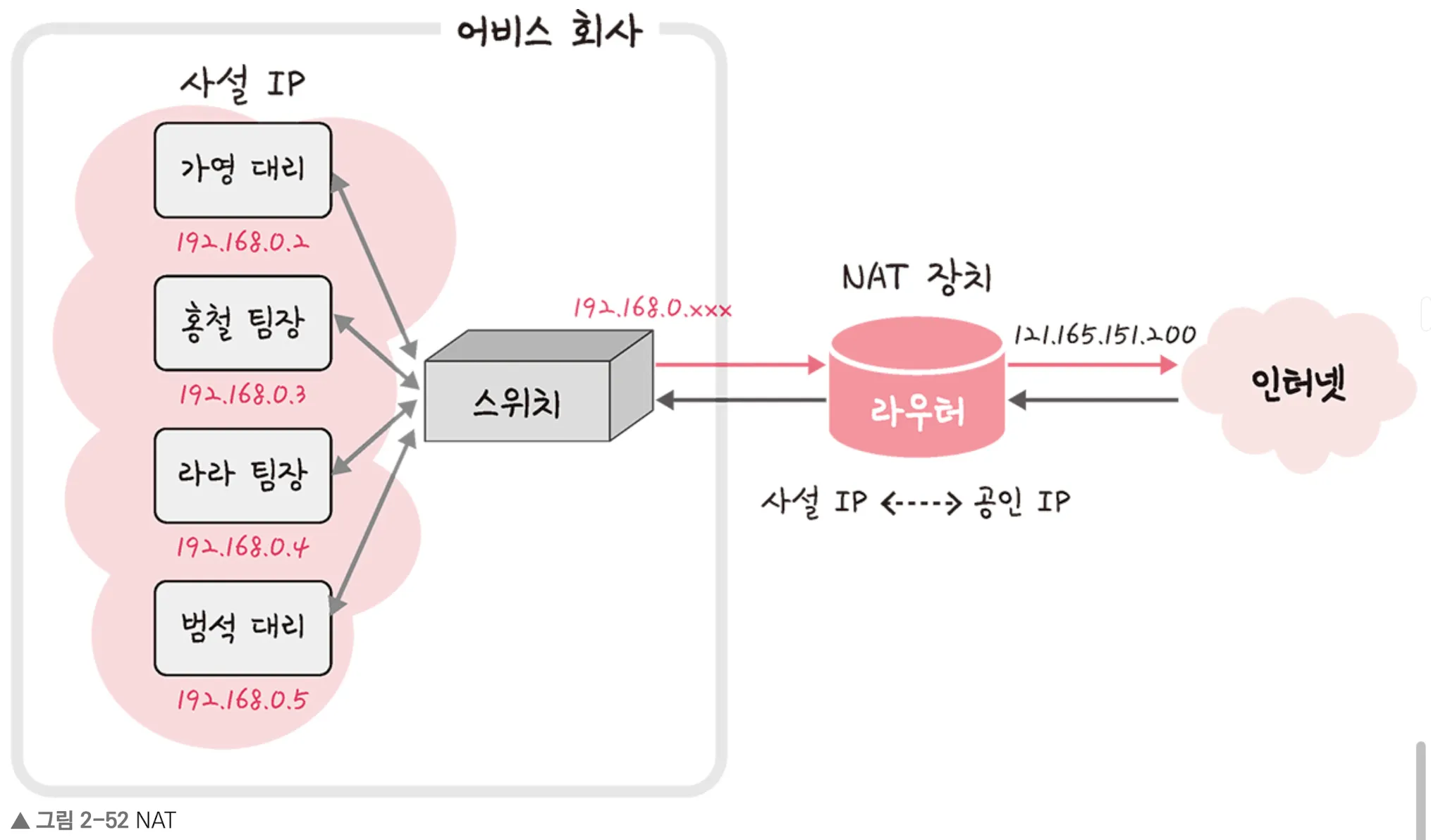
Real-World Example
Suppose two employees (e.g., Manager Hongcheol and Deputy Gayoung) each have private IP addresses like 192.168.0.x.
Using a NAT device, both can access the internet through a single public IP address, such as 121.165.151.200.
- From the internet's perspective, all requests appear to come from the same public IP.
- NAT keeps track of which internal device initiated each request using port numbers and translation tables.
Key Functions of NAT
- Use of Private IP Addresses
- Allows internal networks to use private IP ranges (e.g., 192.168.x.x, 10.x.x.x, 172.16.x.x ~ 172.31.x.x)
- Private IPs are not routable on the public internet and must be translated before leaving the local network.
- IP Address Translation
- NAT converts private IPs to public IPs when data is sent out.
- During response, NAT maps the public IP back to the correct private IP.
- Port Mapping (PAT: Port Address Translation)
- NAT uses port numbers to distinguish between multiple devices using the same public IP.
- Enables multiple hosts to share a single public IP address.
- Security Benefits
- NAT prevents direct access from external hosts to internal devices.
- This acts as a basic firewall, providing an extra layer of security.
Why NAT Is Widely Used
- NAT effectively addresses IPv4 address exhaustion by enabling many devices to share a single public IP.
- It improves security by isolating internal hosts from the public internet.
- As a result, NAT has become one of the most commonly used IP management techniques in modern networking.
Summary:
NAT allows private devices to communicate externally using a single public IP, while offering address conservation, scalability, and basic security.