JTB
2025. 7. 30. 23:14
A process is a program that is currently being executed on a computer.
It is almost the same as a task, which is the unit of work scheduled by the CPU.
When a program is loaded into memory, it becomes an instance of a process,
and then the CPU executes it according to the operating system's scheduler.
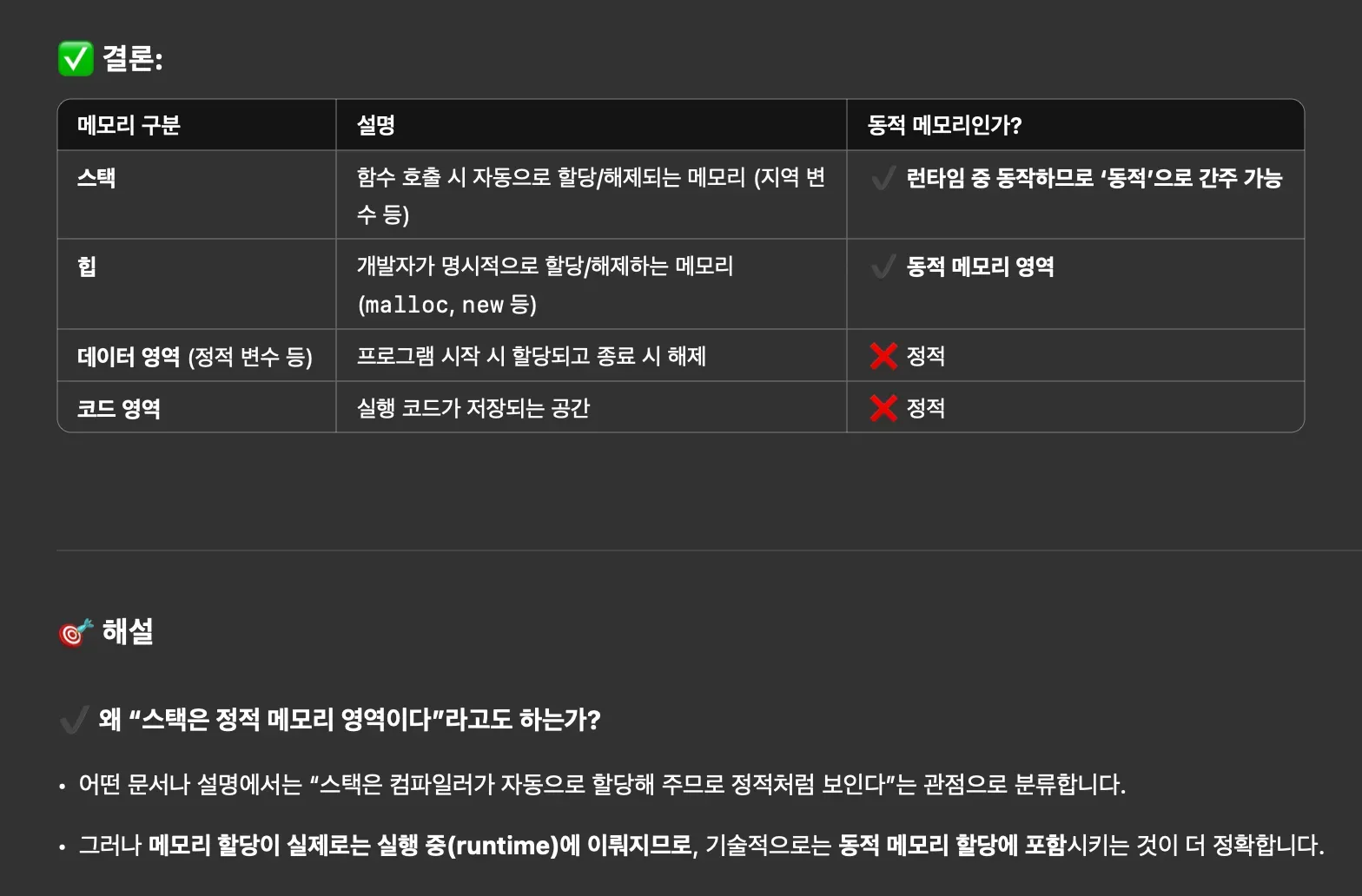
Memory Structure of a Process
When the OS allocates memory to a process, it follows this structure:

Stack and Heap (Dynamic Allocation)
Allocated at runtime.
- Stack: It stores local variables, parameters, and function call information, growing and shrinking as functions are called and return.
- Heap: It stores dynamically allocated data, such as objects and arrays.
Data Segment and Code Segment (Static Allocation)
Allocated at compile time.
- Data Segment:
- BSS Segment: Holds global/static/const variables initialized to 0 or uninitialized.
- Data Segment: Holds global/static/const variables initialized to non-zero values.
- Code Segment: Contains the program’s executable code.