Complexity Analysis?
알고리즘 문제를 풀 때 시간과 공간을 얼마나 차지하는지 보여주는 지표
이는 곧 효율성을 의미한다.
About time complexity...
문제가 커질수록 걸리는 시간이 빠르게, 천천히 또는 거의 변화가 없을수도 있다.
n개의 요소들 중에서 가장 큰 수와 작은 수의 차이를 찾는다.
1. 모든 가능성을 시도할 경우. n^2

2. 가장 큰 수와 작은 수를 찾아 시도할 경우. 2n

3. Sort를 이용하여, 첫번째요소, 마지막요소, 빼기연산 => constant * 시간복잡도 = 3

Big-O Notation
gives an approximation of time complexity
함수 T(n)인 시간복잡도에서 가장 영향력이 큰 부분이 어디인지 따져보는것.

영향력이 가장 큰 차수(최고차항)만을 표현한 것이 빅오 표기법이다. 이 경우,

인데, 앞에 상수가 붙어있더러도 n(데이터 수)의 증가에 따른
연산횟수 증가형태(패턴)는 변하지 않으므로 상수를 생략한다.
O(1) = constant. array lookup, hash table insertion
O(log n) = logarithmic. binary search tree. 시간 복잡도 증가폭이 점점 줄어듬.
O(n) = linear. array 나 linked list에서 특정 요소를 찾을때의 시간 복잡도. gradually increase.
O(n^2) = quadratic. for loop 안에 for loop. 시간 복잡도가 빠르게 증가.
O(C의 n제곱) = exponential. recursion. Fibonacci. 최악의 경우.

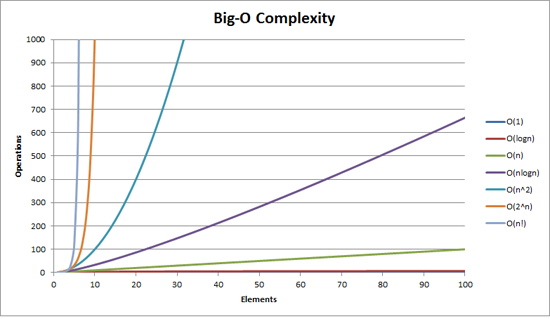
Big O 표기법 상세 설명: zelord.tistory.com/12
Data Structure with Time Complexity
1. Stack
1) Insert: O(1)
2) Remove: O(1)
3) Lookup(position): O(n)
4) find(value): O(n). 탐색을 하거나 값에 접근해야 할때 모든 요소를 확인해야 한다.
2. Queue
1) Insert: O(1)
2) Remove: O(1)
3) Lookup(position): O(n). 탐색을 하거나 값에 접근해야 할때 모든 요소를 확인해야 한다.
4) find(value): O(n). 탐색을 하거나 값에 접근해야 할때 모든 요소를 확인해야 한다.
3. Arrays
(JS가 아닌 다른 언어)Memory 상에서 이어져 있는 자료구조이다(primitive data structure)
contiguous data type.
1) Lookup(position): O(1). 인덱스를 알면 바로 찾아갈 수 있다.
2) Assign: O(1). 인덱스를 사용하여 다른 값을 넣어주면 된다.
3) Insert: O(n). 추가 후 요소들을 한칸씩 이동시켜야 함.
4) Remove: O(n). 삭제 후 요소들을 한칸씩 이동시켜야 함.
5) Find(value): O(n). 처음부터 하나씩 찾아야 함.
4. Linked Lists
non contiguous Data structure 이기 때문에 Head를 반드시 알아야 처음 시작을 할 수 있다.
(doubly linked list의 경우 tail도 알아야 한다.)
value와 next(Singly) 또는 next, previous(doubly) 를 갖는다.
Garbage Collector: reference가 다 끊어져 접근 불가시 garbage collector가 이를 가져가 회수한다.
singly Linked List
1) Lookup: O(n). 메모리가 연속적이지 않기 때문에(random) head부터 reference를 타고 하나씩 확인해야 한다.
2) Assign: O(n). 이유 동일.
3) Find: O(n). 이유 동일.
4) Insert=> O(1). The insertion itself is O(1). Node finding is O(n). 주소만 pointer에 reference하면 된다.
- 마지막에 add하는 경우: O(1)
- 중간에 insert하는 경우: O(1)
5) Remove
- head, tail: O(1)
- middle: O(n). singly linked 의 경우 제거할 요소의 전 요소를 알 수가 없기 때문에 처음(head)부터 찾아야 한다.
doubly Linked List
Remove: O(1). 제거할 요소의 앞 뒤 요소를 알 수 있다. but each node takes up a little more space. Previous 정보를 넣어야 하기 때문이다.
Remove 이외 메소드는 singly linked list와 동일하다.
5. Tree
parent value와 children reference을 갖는다.
ex) DOM Tree.
Normal Tree
Find: O(n). DFS 나 BFS 탐색 여부를 떠나 최악의 경우 모든 요소를 탐색해야 한다.
Binary Search Tree
Find: parent>왼쪽 children, parent<오른쪽 children 조건이 있다.
- O(log n): 밸런스 좋은 경우(right height 과 left height의 차이가 1을 초과하지 않을 경우)
- O(n): 밸런스가 무너진 경우(최악의 경우)


새 노드를 추가할 때마다 밸런스 조정을 해주면 O(log n) 의 더 적은 시간이 소요된다.
Array 와 Binary Tree 에서의 Search 비교
트리의 경우 연속적인 메모리를 차지하지 않기 때문에,
유사한 정렬된 Array에서 insert, remove 할 때보다 더 효율적이다.
6. Hash Table
- 해시 테이블은 배열과 비슷한 형태로 보통 O(1)의 시간 복잡도로 데이터를 조회할 수 있다.
- 같은 키에 너무 많은 요소들이 해시 되어 있으면(데이터충돌) 모든 요소를 확인해야 하기 때문에 많은 시간이 걸린다. O(n).
- 해시 테이블이 로드밸런스(Load Balance)를 초과한 경우, 더 큰 테이블을 만들어 일일이 다시 추가를 해줘야 한다.
- why? 해시 테이블의 공간 사용률이 70% ~ 80%정도가 되면 해시의 충돌이 빈번하게 발생하여 성능이 저하된다.
IT SHOWS EVERYTHING
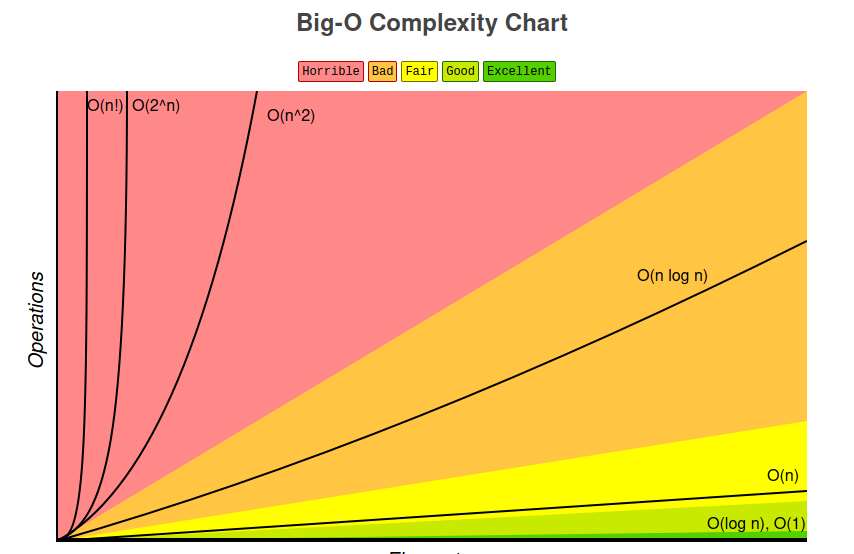

시간복잡도를 그래프로 확인할수 있는 사이트: https://www.desmos.com/calculator/uivk0ucukd?lang=ko
'BootCamp_Codestates > IM Tech Blog' 카테고리의 다른 글
| 8. React Part1 (0) | 2021.01.01 |
|---|---|
| 5. Asynchronous & Promise (0) | 2020.12.21 |
| 3-1. Inheritance Patterns - Subclassing, Prototype Chain (0) | 2020.12.09 |
| 3. Inheritance Patterns - Object Oriented Programming (0) | 2020.12.09 |
| 2-1. Data Structure - Linked-list, HashTable (0) | 2020.12.03 |